What is the Block Editor & How do I use it?
So what’s a block?
Well, a block can be pretty much anything. For example, you can have blocks for:
- Regular text
- Images
- Video embeds
- Buttons
- Widgets (yes, those same widgets you use in your sidebar)
- Tables
- Etc.
Each block is its own entity that you can manipulate on an individual basis. For example, here’s a quick Gutenberg post that contains three blocks:
- 2 text blocks
- 1 image block
Watch how easily I can rearrange those blocks just by dragging and dropping them:
And because each block is “separate”, you can also add things like custom backgrounds just for specific blocks.
In general, it gives you flexibility and in-depth control of how you want your post/page to look.
A quick tour of the WordPress block editor interface
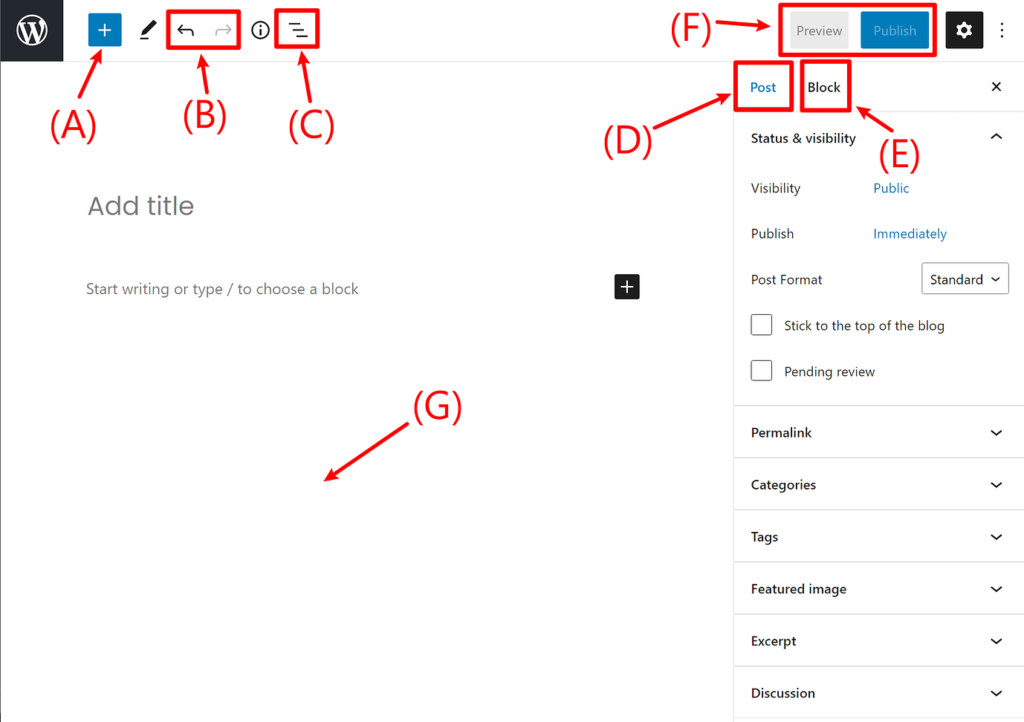
Before you start adding some blocks, let’s go over a quick run-down of the elements of the main block editor interface:
(A) – lets you add new blocks.
(B) – undo/redo buttons
(C) – view a list view (outline) of all your blocks – helpful for quickly navigating between blocks
(D) – gives you access to document settings, covering things like categories & tags, featured images, etc. This is similar to the current sidebar in the WordPress editor
(E) – when you have an individual block selected, this gives you access to settings that are specific to that block
(F) – lets you access a live preview of your post or publish/update your post
(G) – once you add some blocks, this is where you’ll actually work with your post’s content
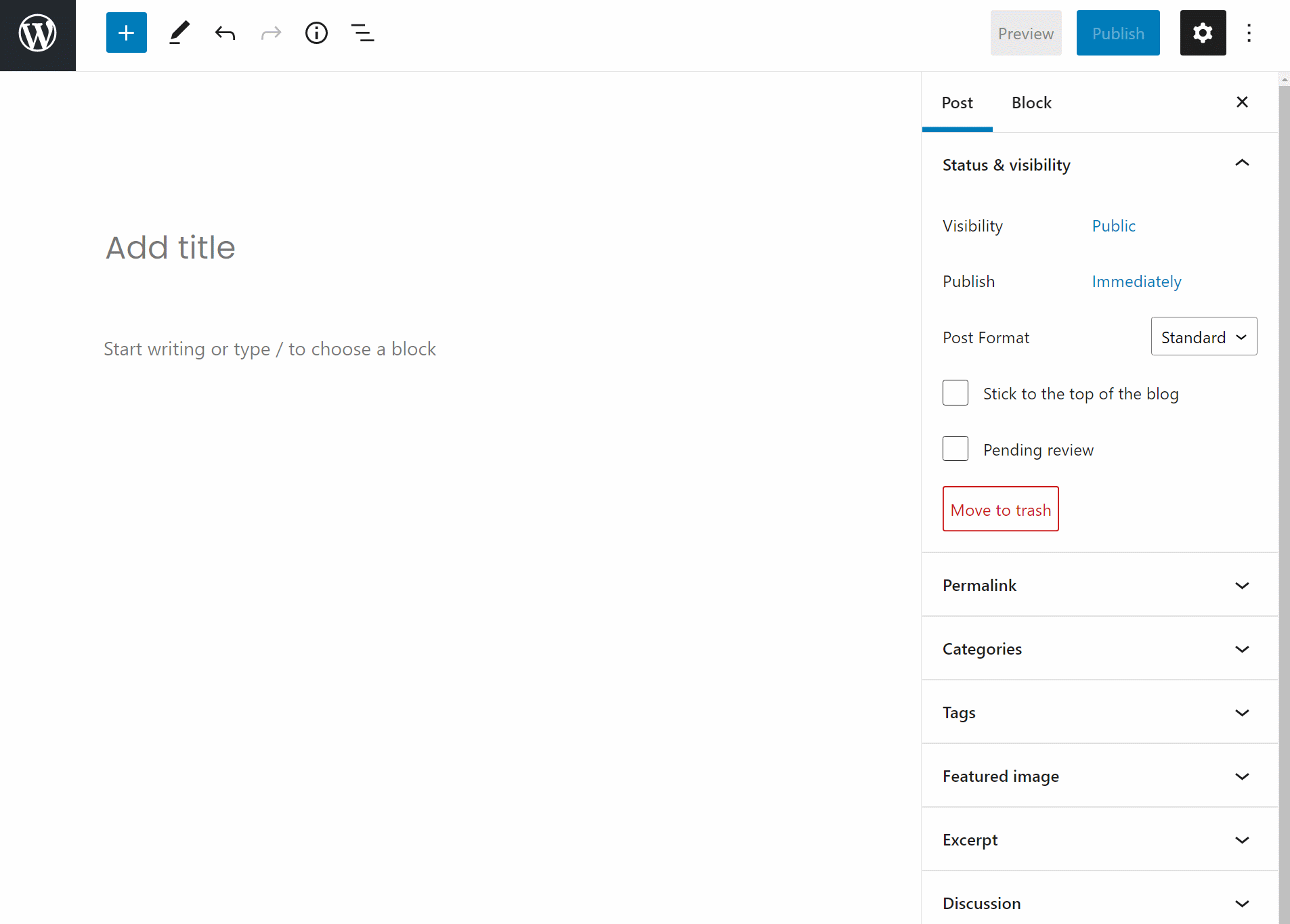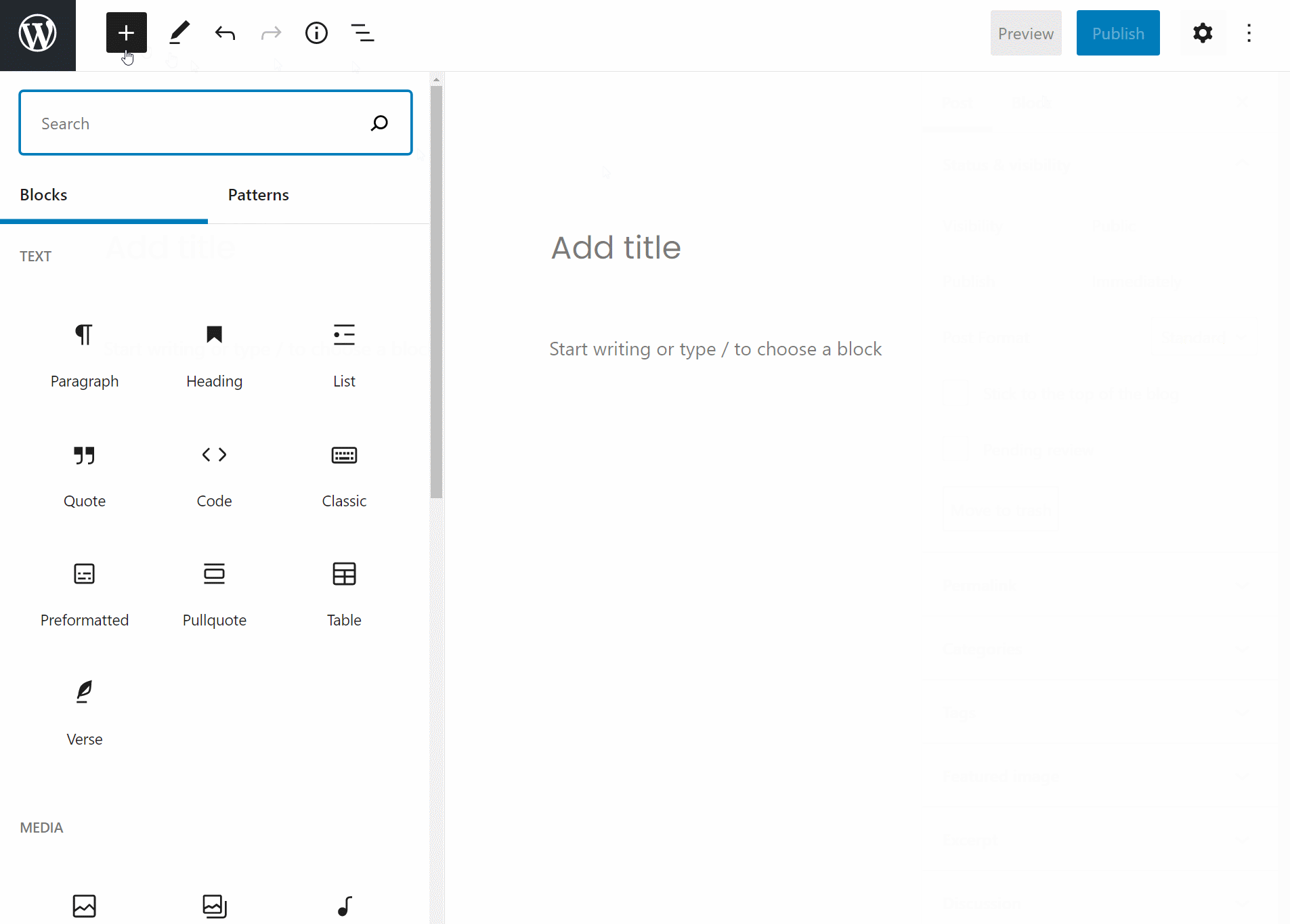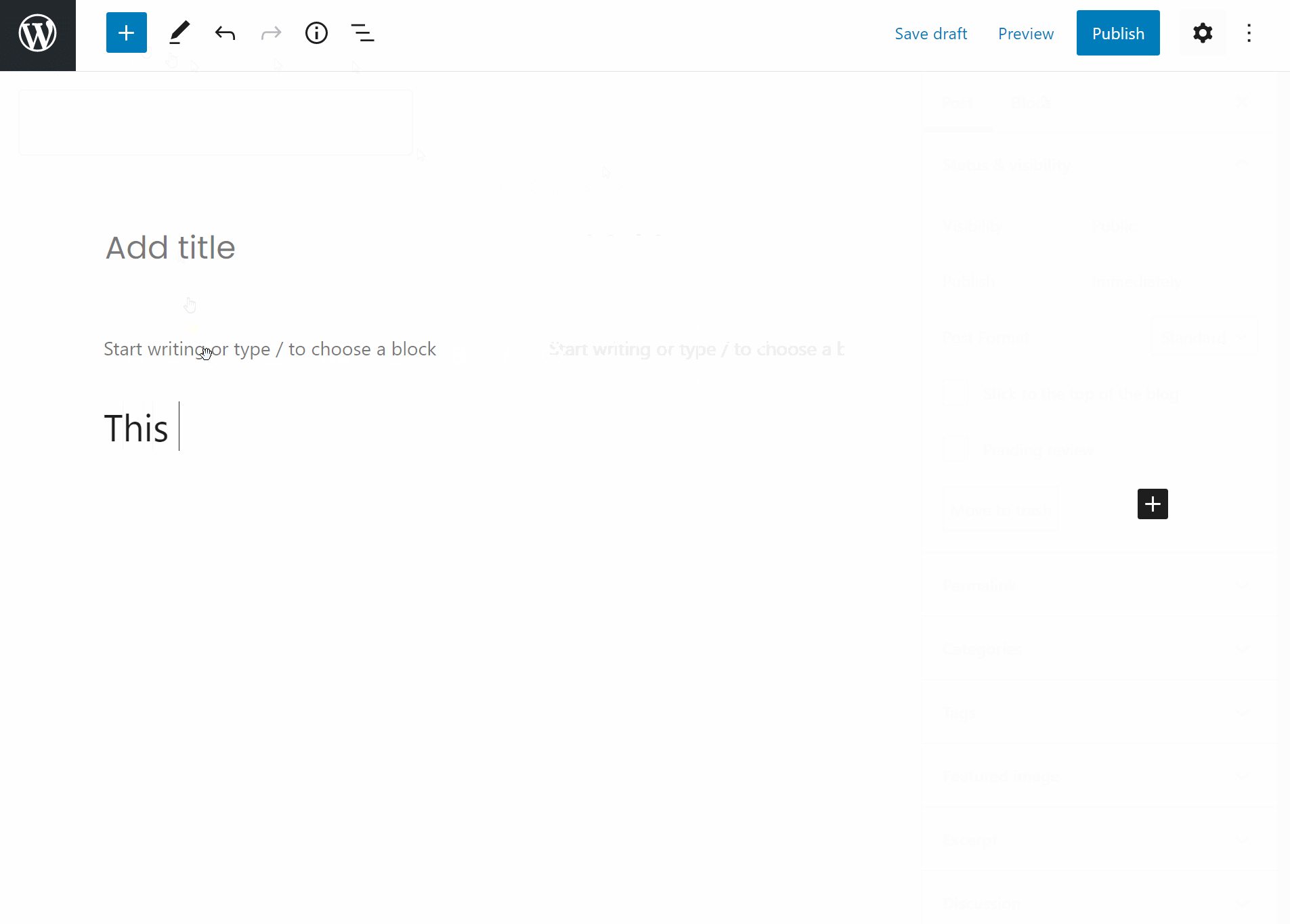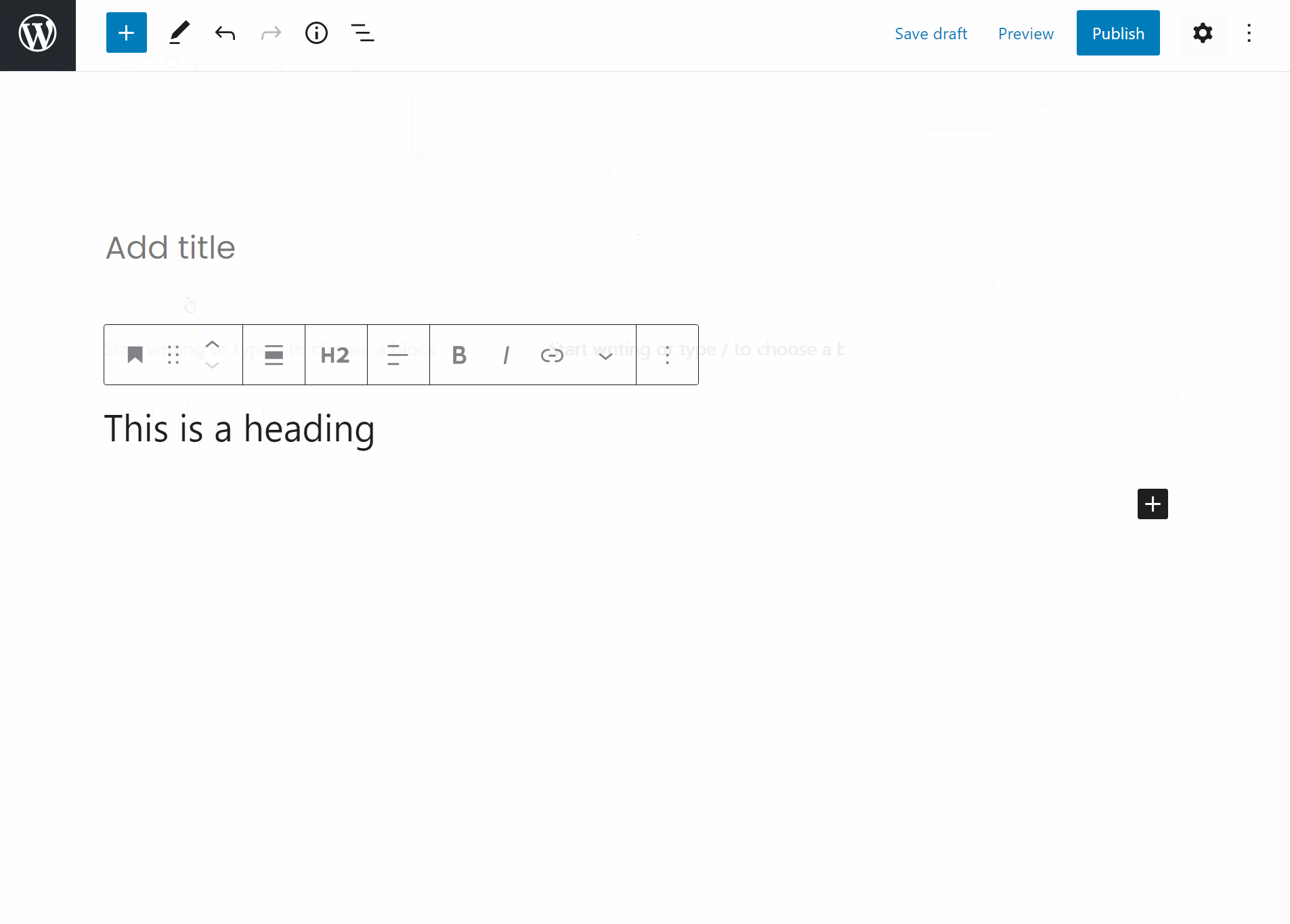
Adding new blocks
As I discussed above, you’ll use separate “blocks” to build your layouts with the editor.
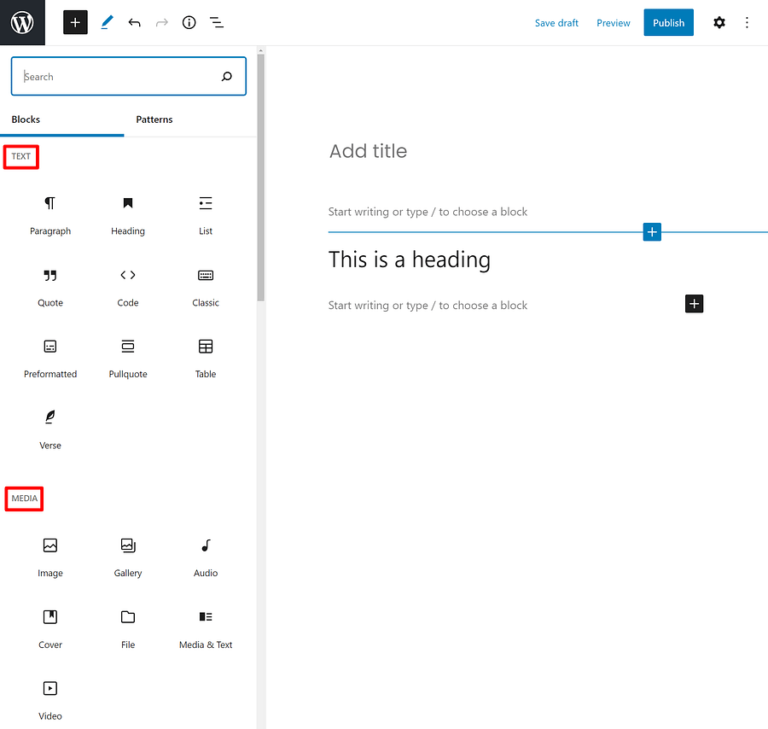
To add a new block, all you need to do is click the +Plus icon and select the type of content you want to add:
In the example above, I showed you how to add a basic paragraph block. But Gutenberg actually includes a ton of different blocks, divided into different sections:
- Text – things like paragraphs, headings, lists, quotes, etc.
- Media – insert images, galleries, videos, audio files, and other media.
- Design – add buttons, columns, sections, spacers, and more.
- Widgets – insert WordPress widgets, such as a list of categories or your latest posts.
- Embeds – embed content from third-party sources like Twitter, YouTube, Spotify, Vimeo, and others.
Putting it all together
Once you pick up the flow of how things work with the block editor, it’s fairly painless and intuitive.
At first, you might experience some growing pains and struggle to perform basic actions that you’ve taken for granted. But once you get the hang of things – you should be cruising through building layouts.